

REDARC's BCDC Charging Process Explained
Three Stage Charging Process
Boost Stage Absorption Stage Float Stage
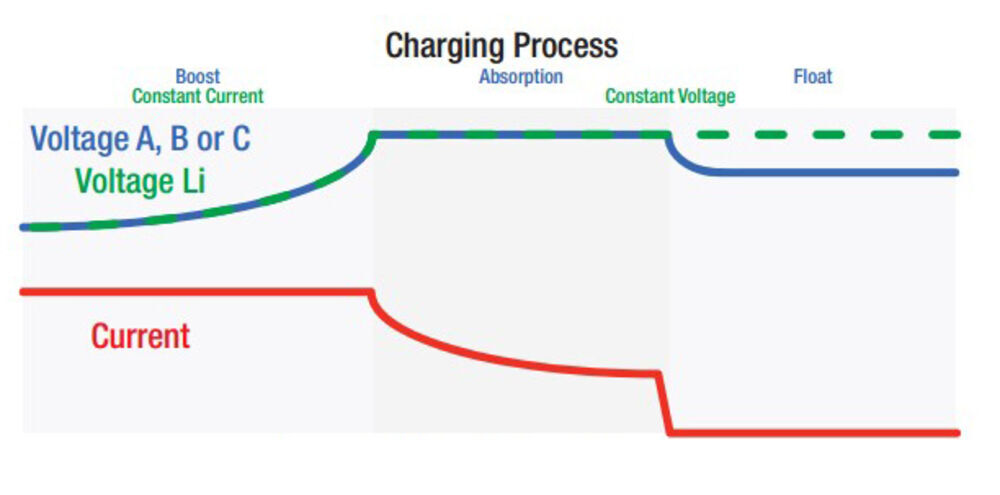
Two Stage Charging Process (Lithium)
Constant Current Constant Voltage

Departments
Towing
- Trailer Hitch
- Fifth Wheel
- Gooseneck
- Towing a Vehicle
- Front Hitch
- RV Hitch
- ATV Hitch
- HD Truck Hitch
- Vehicle Wiring
- Brake Controller
- Ball Mounts
- Weight Distribution
Sports and Recreation
Trailer Parts
- Utility Trailer
- Boat Trailer
- Landscape Trailer
- Enclosed Trailer
- 5th/Camper Trailer
- Car Hauler
- Horse Trailer
Vehicle
Contact & Help

What our customers are saying:
"Easy place to shop. Fast delivery and great products. Very happy with my purchase."
Ed
Boynton Beach, FL
Popular Vehicles
- Subaru Forester
- Ford F-350 Super Duty
- Ford F-250 Super Duty
- Chevrolet Silverado 1500
- Jeep Wrangler Unlimited
- Jeep Wrangler
- Ram 3500
- Toyota Highlander
- Ram 2500
- Chevrolet Silverado 2500
- Subaru Outback Wagon
- Chevrolet Silverado
- Dodge Ram Pickup
- GMC Sierra 2500
- Ram 1500
- Ford F-250 and F-350 Super Duty
- Jeep Grand Cherokee
- Toyota Tacoma
- GMC Sierra 3500
- Toyota Tundra
- Ford Escape
- More >>

























Tom E.
6/17/2022
The article does answer the question of what a DC to DC charger is and how they work. Good article.